A neural network improves forecasts for severe storm hazards
The Nationwide Middle for Atmospheric Analysis (NCAR) is utilizing synthetic intelligence to run experimental forecasts for hail, tornadoes, and intense winds—storm hazards that may trigger critical harm however which can be notoriously troublesome for climate fashions to precisely predict.
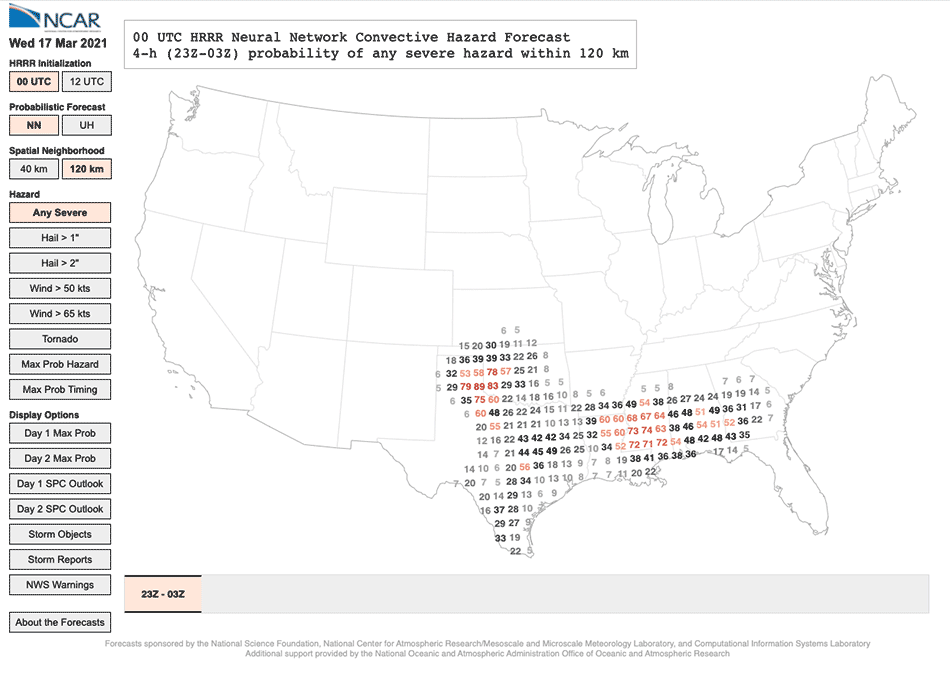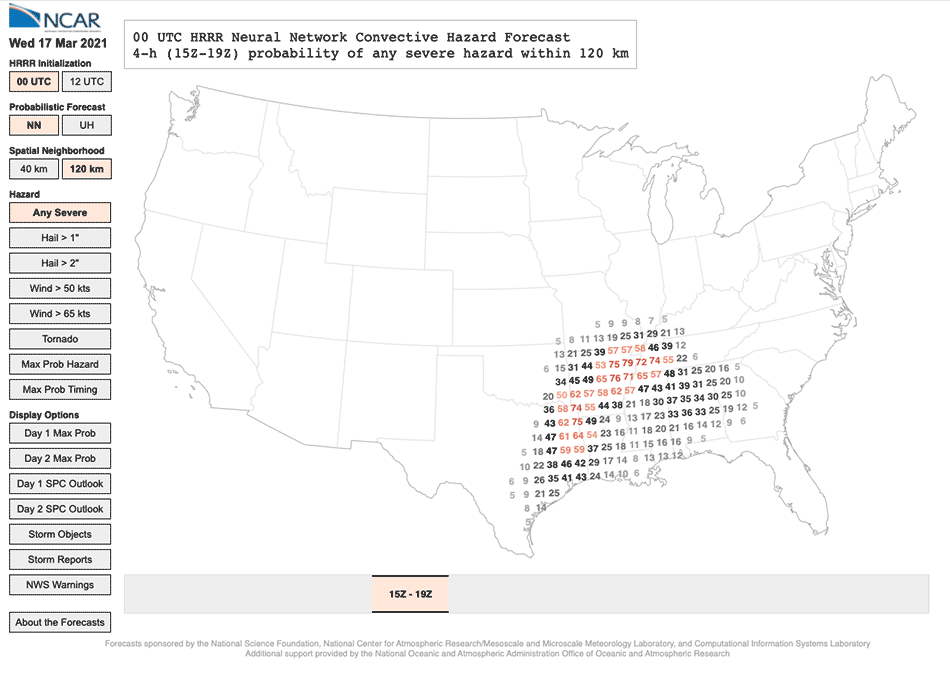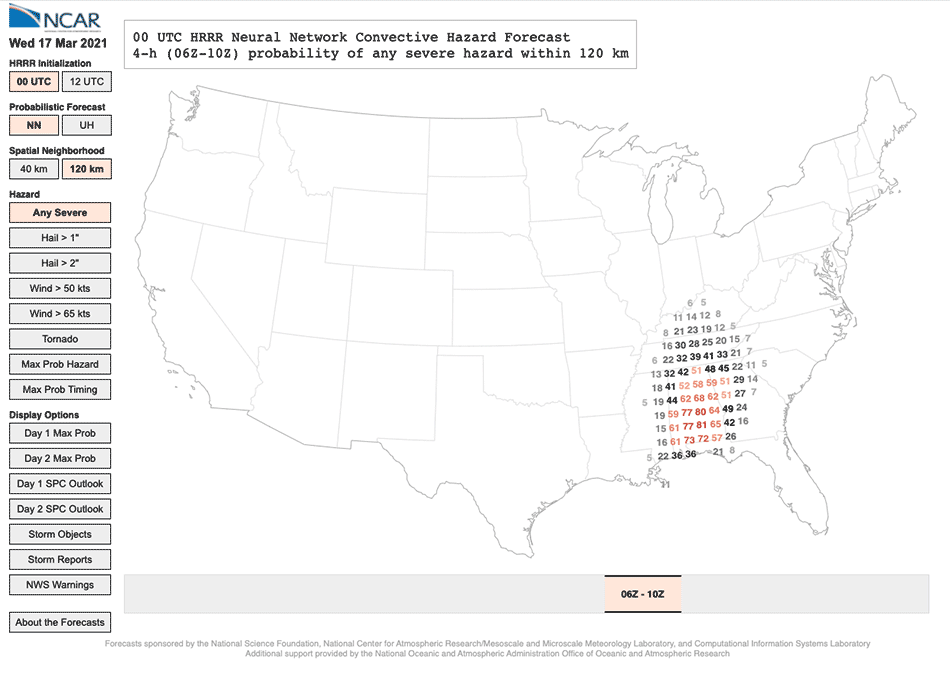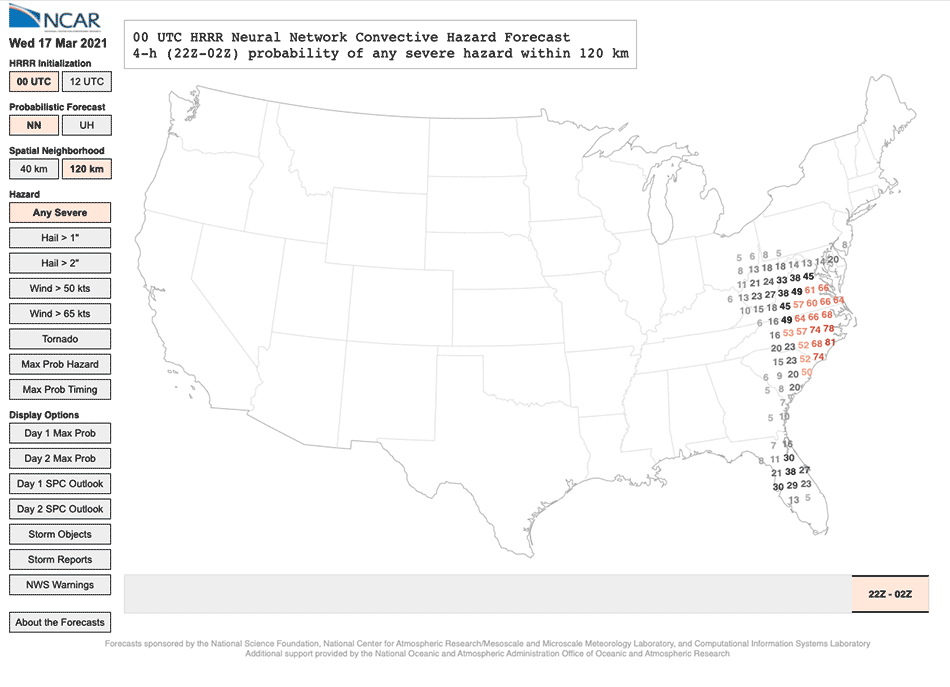
The Neural Community Convective Hazard Forecasts, which offer the chance of hail, tornadoes, or winds for a selected location at a selected time, are up to date twice day by day and freely out there on-line.
NCAR started working these analysis forecasts within the spring of 2020 as a part of the Hazardous Climate Testbed Spring Experiment on the Nationwide Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). When the spring extreme climate season wrapped up on the finish of June, the analysis group analyzed the forecasts, evaluating them to extra conventional strategies for forecasting storm hazards. The scientists discovered that the neural community considerably improved the accuracy of forecasts based mostly on conventional mannequin output, particularly in conditions the place these conventional forecasts tended to carry out the worst, together with within the jap and western components of the US and for nighttime storms.
“We have been in a position to present a big enchancment in most conditions,” mentioned NCAR scientist Ryan Sobash, who’s main the undertaking. “Not solely did the neural community extra skillfully predict when and the place extreme storm hazards have been possible, it was additionally in a position to higher predict whether or not the hazardous occasion can be dominated by hail or by winds.”
The system is up and working once more this spring with some tweaks. The undertaking is being funded by NOAA and the Nationwide Science Basis, which is NCAR’s sponsor. The forecasts are run on the Cheyenne supercomputer on the NCAR-Wyoming Supercomputing Middle.
From one predictor to 40
To ensure that a climate mannequin to spin up a thunderstorm, it needs to be run at a excessive sufficient decision to seize the fine-scale atmospheric phenomena—together with updrafts and downdrafts—that drive the storm’s creation. This usually requires spacing of 4 kilometers (2.5 miles) or much less between grid factors contained in the mannequin. At that decision, the mannequin can start to simulate the storm itself, however it’s unable to supply most of the hazards related to the storm, which occur at even smaller scales, together with hailstones and tornadoes. Due to that, forecasters have relied on specific outputs within the mannequin information, or proxies, to find out the probability {that a} extreme storm will produce such hazards.
One of the vital steadily used proxies is updraft helicity, a measure of a storm’s rotation. Storms with stronger rotation are usually extra extreme and extra able to producing hail and tornadoes. This proxy has labored comparatively effectively for supercells and different rotating storms, nevertheless it would not seize a number of the extreme climate that may be produced in straight-line storms, similar to derechos.
In contrast, the neural community utilized in NCAR’s new forecasts can ingest about 40 various factors, together with updraft helicity but in addition the storm’s location, time, dew level, wind speeds, floor strain, and way more. The neural community makes use of patterns in how these predictors relate to 1 one other that it gleaned from its coaching information set—on this case practically 500 previous forecasts from NOAA’s Excessive-Decision Fast Refresh mannequin together with the accompanying stories of precise storms—to calculate the chance {that a} storm will produce hail, tornadoes, or sturdy winds. The forecasts produced by the neural networks present the probability of a storm hazard forming inside both 40 kilometers (25 miles) or 120 kilometers (75 miles) of particular person grid factors within the mannequin.
By making an allowance for elements past storm rotation, the neural community is healthier in a position to predict hazards related to straight-line wind storms than forecasts based mostly solely on updraft helicity, and it additionally improves on forecasts for areas the place supercells are usually not as prone to kind, particularly areas outdoors the Midwest.
“The success of our neural community forecast means that machine studying might be a great tool for operational forecasts,” Sobash mentioned. “The forecasts are being run once more this spring as a part of the Hazardous Climate Testbed and we sit up for getting extra suggestions from the operational forecasters about how they may incorporate this sort of info into their present forecasting course of.”
Conclusion: So above is the A neural network improves forecasts for severe storm hazards article. Hopefully with this article you can help you in life, always follow and read our good articles on the website: Ngoinhanho101.com