An artificial intelligence tool that can help detect melanoma
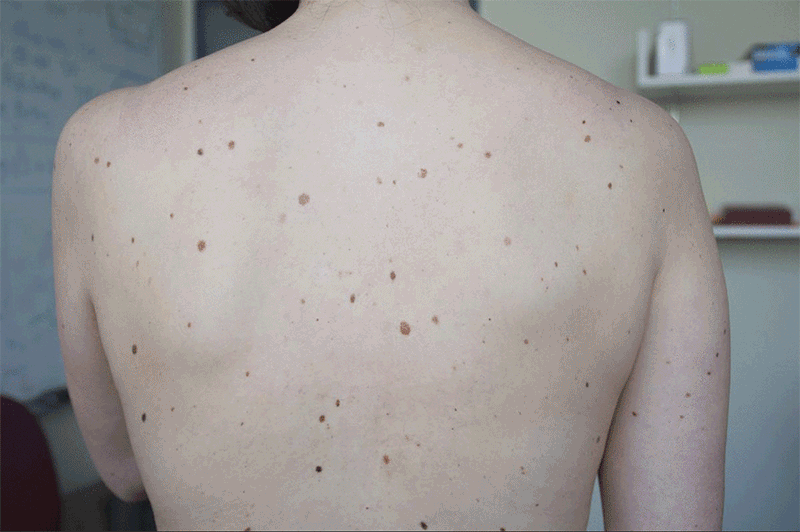
Melanoma is a kind of malignant tumor chargeable for greater than 70 p.c of all pores and skin cancer-related deaths worldwide. For years, physicians have relied on visible inspection to determine suspicious pigmented lesions (SPLs), which will be a sign of pores and skin most cancers. Such early-stage identification of SPLs in main care settings can enhance melanoma prognosis and considerably cut back remedy value.
The problem is that shortly discovering and prioritizing SPLs is troublesome, as a result of excessive quantity of pigmented lesions that usually have to be evaluated for potential biopsies. Now, researchers from MIT and elsewhere have devised a brand new synthetic intelligence pipeline, utilizing deep convolutional neural networks (DCNNs) and making use of them to analyzing SPLs by the usage of wide-field images frequent in most smartphones and private cameras.
DCNNs are neural networks that can be utilized to categorise (or “title”) photographs to then cluster them (corresponding to when performing a photograph search). These machine studying algorithms belong to the subset of deep studying.
Utilizing cameras to take wide-field images of huge areas of sufferers’ our bodies, this system makes use of DCNNs to shortly and successfully determine and display screen for early-stage melanoma, in keeping with Luis R. Soenksen, a postdoc and a medical gadget professional at present appearing as MIT’s first Enterprise Builder in Synthetic Intelligence and Healthcare. Soenksen carried out the analysis with MIT researchers, together with MIT Institute for Medical Engineering and Science (IMES) school members Martha J. Grey, W. Kieckhefer Professor of Well being Sciences and Expertise, professor {of electrical} engineering and laptop science; and James J. Collins, Termeer Professor of Medical Engineering and Science and Organic Engineering.
Soenksen, who’s the primary writer of the latest paper, “Utilizing Deep Studying for Dermatologist-level Detection of Suspicious Pigmented Pores and skin Lesions from Large-field Photos,” revealed in Science Translational Drugs, explains that “Early detection of SPLs can save lives; nevertheless, the present capability of medical methods to offer complete pores and skin screenings at scale are nonetheless missing.”
The paper describes the event of an SPL evaluation system utilizing DCNNs to extra shortly and effectively determine pores and skin lesions that require extra investigation, screenings that may be performed throughout routine main care visits, and even by the sufferers themselves. The system utilized DCNNs to optimize the identification and classification of SPLs in wide-field photographs.
Utilizing AI, the researchers skilled the system utilizing 20,388 wide-field photographs from 133 sufferers on the Hospital Gregorio Marañón in Madrid, in addition to publicly obtainable photographs. The photographs had been taken with a wide range of unusual cameras which can be available to shoppers. Dermatologists working with the researchers visually categorized the lesions within the photographs for comparability. They discovered that the system achieved greater than 90.3 p.c sensitivity in distinguishing SPLs from nonsuspicious lesions, pores and skin, and sophisticated backgrounds, by avoiding the necessity for cumbersome and time-consuming particular person lesion imaging. Moreover, the paper presents a brand new technique to extract intra-patient lesion saliency (ugly duckling standards, or the comparability of the lesions on the pores and skin of 1 person who stand out from the remainder) on the idea of DCNN options from detected lesions.
“Our analysis means that methods leveraging laptop imaginative and prescient and deep neural networks, quantifying such frequent indicators, can obtain comparable accuracy to professional dermatologists,” Soenksen explains. “We hope our analysis revitalizes the need to ship extra environment friendly dermatological screenings in main care settings to drive ample referrals.”
Doing so would enable for extra fast and correct assessments of SPLS and will result in earlier remedy of melanoma, in keeping with the researchers.
Grey, who’s senior writer of the paper, explains how this necessary challenge developed: “This work originated as a brand new challenge developed by fellows (5 of the co-authors) within the MIT Catalyst program, a program designed to nucleate tasks that resolve urgent scientific wants. This work exemplifies the imaginative and prescient of HST/IMES devotee (by which custom Catalyst was based) of leveraging science to advance human well being.” This work was supported by Abdul Latif Jameel Clinic for Machine Studying in Well being and by the Consejería de Educación, Juventud y Deportes de la Comunidad de Madrid by the Madrid-MIT M+Visión Consortium.
Conclusion: So above is the An artificial intelligence tool that can help detect melanoma article. Hopefully with this article you can help you in life, always follow and read our good articles on the website: Ngoinhanho101.com