10 Ways to Boost Your Wi-Fi Signal
Browsing at a snail’s pace, the inability to stream, dropped Wi-Fi signals, and wireless dead zones—all of these issues are aggravating in a world where getting online has become as important as breathing for some. (Okay, so it’s not that critical…but it’s still significant.)
There are a variety of programs available to if you believe it has become sluggish. You can also attempt a few ways to troubleshoot your network issues. If standing next to your wireless router is the only way you can get acceptable reception, these easy tips can help you optimize your network.
Contents
- 1 1. Make sure you have a wired internet connection.
- 2 2. Update the Firmware on Your Router
- 3 3. Obtain Optimal Router Positioning
- 4 4. Do You Have a Frequency?
- 5 5. Switch to another channel
- 6 6. Defend Against Wi-Fi Intruders
- 7 7. Maintain Quality
- 8 8. Get a New Antenna
- 9 9. Replace any obsolete hardware.
- 10 10. Extend your Wi-Fi range with a Range Extender or Mesh Wi-Fi
1. Make sure you have a wired internet connection.
Before you blame the Wi-Fi, double-check that the internet coming into your home is working properly. If your laptop doesn’t have an Ethernet port, use an Ethernet cable to connect it to your modem. If your laptop doesn’t have an Ethernet port, you’ll need a USB to Ethernet adapter.
To find out how fast your internet is, take a speed test. You may need to contact your ISP or change your modem if it does not match the speed on your internet bill. If your speed test and internet bill match, but your internet still seems slow, it may be time to upgrade to a better plan. (When I told my grandma that her Wi-Fi was broken, she thought it was because she was on a 3Mbps connection.)
If the modem appears to be in good working order, repeat the test wirelessly while standing right near to the router. If you obtain identical speeds near the router but not elsewhere in the house, it’s possible that your Wi-Fi coverage is to blame. If your internet is still slow when you’re standing directly close to the router, you may need to improve your equipment.
2. Update the Firmware on Your Router
It’s a good idea to update your router before you start tinkering. Software is always being improved by router manufacturers in order to gain a little more speed. The ease with which you can change your firmware is entirely dependent on the manufacturer and type of your device.
Most modern routers have the firmware upgrade process incorporated right into the management interface, so it’s as simple as pressing a button. Some older models still require you to go to the manufacturer’s website, download a firmware file from your router’s support page, and upload it to the administrator interface. It’s laborious, but it’s still a fantastic idea because it’s such a straightforward remedy.
Even if your wireless network is in good shape, you should upgrade your firmware on a regular basis for speed enhancements, new features, and security updates. We offer a guide on how to access your router’s settings if you need it.
The adventurous should check at a third-party firmware like the open-source DD-WRT if they really want to get the most out of their present router. This can improve performance and provide access to more complex networking functions, such as the ability to set up a virtual private network (VPN) directly on your router. It’s a little more difficult to set up, but it might be worth it for tech-savvy individuals.
3. Obtain Optimal Router Positioning
The Wi-Fi signal will not be distributed evenly throughout all homes. The truth is that the location of your router has a significant impact on your wireless coverage. Although it may appear reasonable to place the router inside a cabinet and out of the way, or near the window where the cable enters, this is not always the case. Rather than being placed at the far end of your house, the router should be placed in the middle, if feasible, so that its signal may easily reach all four corners.
Furthermore, wireless routers require open locations free of walls and barriers. While it may be tempting to hide that unsightly black box under a stack of books, you’ll receive a better signal if it’s in the open (which should prevent the router from overheating, too). It’s also a good idea to keep it away from any heavy-duty appliances or electronics, as doing so can affect Wi-Fi performance. You can boost performance significantly by removing even one wall between your workspace and the router.
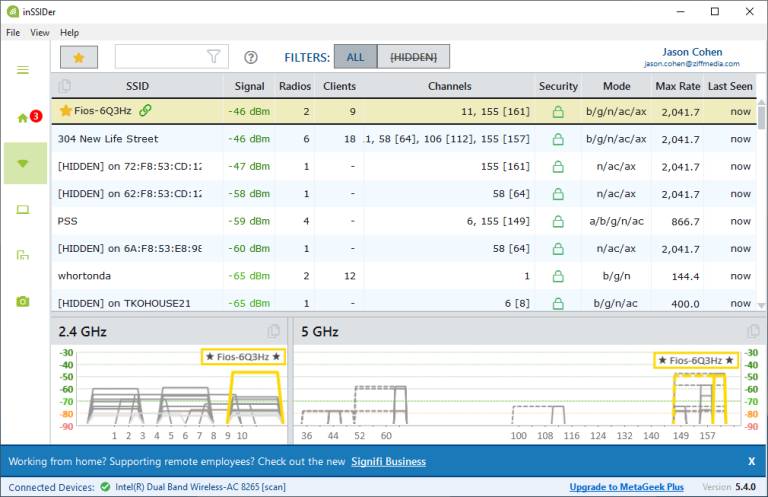
If your router has external antennae, make sure they’re oriented vertically to improve coverage. If possible, elevate the router by mounting it high on the wall or on the top shelf to improve the signal. There are numerous tools available to assist you in visualizing your network coverage. We recommend Ekahau’s Heatmapper and MetaGeek’s , which show you your Wi-Fi network’s weak and strong points. Mobile apps, such as , are also available.
4. Do You Have a Frequency?
Examine your network’s administrator interface to ensure that it is set up for optimal performance. If you have a dual-band router, switching to the 5GHz band instead of the more popular 2.4GHz band will likely improve throughput.
Because the 5GHz band is not as widely utilized as the 2.4GHz frequency, you’ll likely see less interference from other wireless networks and devices. (It doesn’t handle barriers and distances as well as a 2.4GHz signal, so it won’t necessarily travel as far.)
The majority of new dual-band routers should allow you to use the same network name, or SSID, on both bands. Look for the 5GHz network option in your router’s management interface, and give it the same SSID and password as your 2.4GHz network. As a result, your devices will automatically select the best signal available whenever possible.
(If your router doesn’t allow you to use the same SSID, give it a different name, such as SmithHouse-5GHz, and try to connect to it manually whenever feasible.)
5. Switch to another channel
Interference is a significant problem, particularly for people who reside in heavily crowded places. Other wireless networks, as well as some cordless phone systems, microwaves, and other electronic equipment, might slow down speeds.
Have you ever used walkie-talkies as a kid? You may recall that in order to hear each other, the units had to be on the same “channel.” You could also listen in on someone else’s discussion if you were on the same channel as your neighbors, even if they were using a different set. In a similar spirit, when talking with your devices, all current routers may switch between several channels.
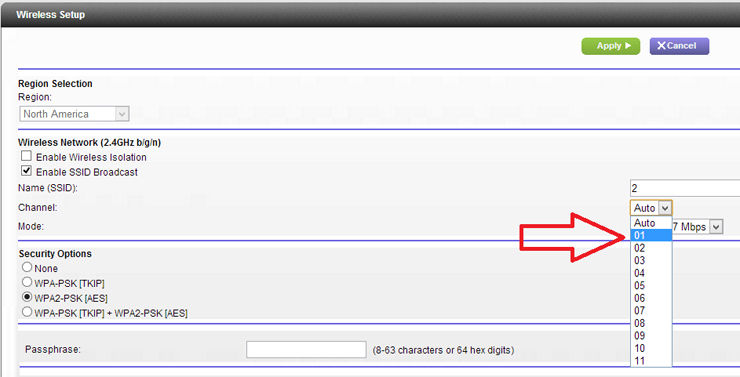
Most routers will determine the channel for you, but if other wireless networks use the same channel as you, signal congestion will occur. When set to Automatic, a decent router will try to select the least crowded channel, while older or less expensive routers may just select a predefined channel, even if it isn’t the best. That might be an issue.
You can view what channels nearby Wi-Fi networks are using on Windows-based PCs. Type netsh wlan show all from the command prompt to get a list of all wireless networks and channels active in your area. The aforementioned network analyzers can also display this information, frequently in a graphical style that is easier to understand.
Most of our networks, as well as those of our neighbors, use channels 6 and 11 at the PCMag office. In general, adhere to channels 1, 6, and 11 for 2.4GHz because they’re the only ones that don’t overlap with other channels (which can degrade performance). However, because 5GHz employs non-overlapping channels, picking the proper one should be much easier.
If the Auto setting isn’t working for you, log into your router’s administrator interface, go to the basic wireless category, and choose one manually (preferably one that isn’t shared by a lot of other networks in your vicinity). Run another speed test to see if the Manual setting delivers a better signal and faster speeds in your problem locations than the Automatic setting.
Keep in mind that channel congestion can change over time, so if you manually select a channel, you may want to check in every now and then to be sure it’s still the best option.
6. Defend Against Wi-Fi Intruders
It’s likely that the issue has nothing to do with Wi-Fi range or interference. You could have an uninvited guest or two piggybacking on your network if your network is open or has a weak password. Your video chats will suffer if your neighbor is downloading numerous 4K movies on your Wi-Fi.
These tools can help you find a list of devices connected to your Wi-Fi network, which can help you spot unexpected guests. Your router’s admin interface may also have a traffic analyzer that will show you which devices are consuming a lot of data—you might even discover one of your own children is hogging bandwidth without your knowledge. (If that’s the case, here’s how to get rid of them.)
After you’ve found the intruder and fixed the problem, lock down your network with a strong password—preferably WPA2, as WEP is infamously simple to crack—so that no one else may join.
7. Maintain Quality
Like the Netgear menu above, most current routers come with Quality of Service (QoS) features to control the amount of bandwidth that apps utilize. You could, for example, utilize QoS to prioritize video calls over file downloads, ensuring that your connection with Grandma doesn’t drop merely because someone else is downloading a large file from Dropbox. (Yes, their file will take longer, but Grandma comes first.) You can also prioritize different apps at different times of the day using some QoS settings.
In the network administrator interface, QoS options are usually available under advanced settings. Some routers may even make it easier by allowing you to prioritize multimedia or gaming applications with a single click. There are actions you can take to make things better if you’re trying to stream games while sharing a network.
8. Get a New Antenna
If your router has an internal antenna, replacing it with an exterior one is a smart idea because the latter sends a better signal. Many router manufacturers sell antennas separately if your router did not come with antennae that you may add on yourself (or if you threw them away long ago).
In many circumstances, you can select between omnidirectional antennas, which broadcast a signal in all directions, and directional antennas, which broadcast a signal in one direction only. Because most built-in antennas are omnidirectional, if you buy an external antenna, be sure it says “high-gain” on the package.
Because you’re unlikely to have weak areas in your network in every direction, a directional antenna is a superior choice. If you point your external antenna in the direction of your weak spot, the signal will be disseminated in that direction. For further information on what to buy, go to the website of the router’s manufacturer.
9. Replace any obsolete hardware.

It’s a good idea to get the most out of your existing equipment, but you can’t expect the best performance if you’re using obsolete technology. With back-end devices, particularly networking hardware, we have a propensity to follow the “if it ain’t busted, don’t fix it” mindset. However, if you bought your router a long time ago, it’s possible that you’re still using the slower 802.11n standard (or God forbid, 802.11g).
Older routers may have lower bandwidth limits and even narrower ranges. As a result, all of the aforementioned tuning will only get you so far—the maximum speed for 802.11g is 54Mbps, while the maximum throughput for 802.11n is 300Mbps. The latest 802.11ac routers support 1 gigabit per second, whereas Wi-Fi 6 routers can theoretically reach 10 gigabits per second. If you’re looking for a speedier network, start with our list of the best wireless routers.
Even if your router is brand new, you may have some older devices that are reverting to slower standards. You probably have an 802.11ac wireless adapter, or at the very least an 802.11n wireless adapter, if you bought a PC in the previous couple of years. However, the older your devices are, the less likely they are to be equipped with new technology. (However, you might be able to buy a USB Wi-Fi adapter to improve things on those old devices.)

TP-Link Archer AX11000 Next-Gen Tri-Band Gaming Router

Asus ROG Rapture GT-AC5300

Asus ZenWiFi ET8
Remember that a higher-quality router will not only handle those quicker standards, but will also perform better in all of the other areas we’ve discussed. It will have improved channel selection, greater band steering for 5GHz devices, and improved QoS features.
Others, such as the Editors’ Choice TP-Link Archer AX11000 tri-band gaming router, may contain capabilities like Multi User-Multiple Input Multiple Output (MU-MIMO). MU-MIMO routers can send and receive multiple data streams to numerous devices at the same time without degrading bandwidth, however they require specialist testing with multiple clients, which must be MU-MIMO compatible.
If you do decide to purchase a new router, the setup process will be simple. We offer a setup and configuration guide for the device.
10. Extend your Wi-Fi range with a Range Extender or Mesh Wi-Fi
Although some modern routers may have better range than your old beater, you may still be unable to acquire the range you require in many homes. If the network has to cover a bigger area than the router can broadcast to, or if there are a lot of corners to go around and walls to break through, performance will suffer. If none of the previous suggestions work, it’s conceivable that your home is simply too huge for a single router to deliver a strong signal to everyone. You’d need another device to extend your signal in that instance.
Range extenders accept a signal from your network and rebroadcast it to your devices, as well as the other way around. While they’re less expensive, mesh Wi-Fi systems, which replace your existing router totally, are often more effective. Multiple devices operate together to intelligently route data back to your modem, blanketing your house in a single Wi-Fi network that covers anywhere you need.
When placing these mesh points, follow the same guidelines for determining placement: one node should be linked to your modem, and the others should be close enough to pick up a solid signal while still being far enough away to cover dead zones.

Asus ZenWiFi ET8

Netgear Orbi RBKE963 WiFi 6E Mesh System

TP-Link Deco M9 Plus Mesh Wi-Fi System
Wi-Fi mesh systems have always had the disadvantage of being more expensive than just adding a range extender to your current router. However, Amazon’s Eero 6 and Eero Pro 6 routers, which cost roughly $100 to $200 less than many of its mesh competition while boasting Wi-Fi 6 compatibility and even a Zigbee smart home device hub incorporated into the main router, are expected to change that in the near future.
Note that even with a mesh system, there may be some performance loss on the far ends of your house, especially if your Wi-Fi has to make multiple “hops”—again, placing the main unit in the center of your house and connecting the nodes with Ethernet will yield the best results. Trust me when I say that if you truly want trouble-free Wi-Fi, having an electrician run a couple of Ethernet wires to each mesh device is worth it, because anything else, in my view, is a compromise that may or may not meet your expectations.
Mesh Wi-Fi systems are not inexpensive, especially if you have a large home with several nodes. However, if you’re in the market for a new router anyway, they’re a viable option. If you’re tech-savvy, you might be able to save money by setting up a few Ubiquiti UniFi Lite access points, which are less expensive but more complex.
Conclusion: So above is the 10 Ways to Boost Your Wi-Fi Signal article. Hopefully with this article you can help you in life, always follow and read our good articles on the website: Ngoinhanho101.com